Frontiers | EMT-Mediated Acquired EGFR-TKI Resistance in NSCLC: Mechanisms and Strategies | Oncology

Erlotinib Directly Inhibits HER2 Kinase Activation and Downstream Signaling Events in Intact Cells Lacking Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Expression | Cancer Research

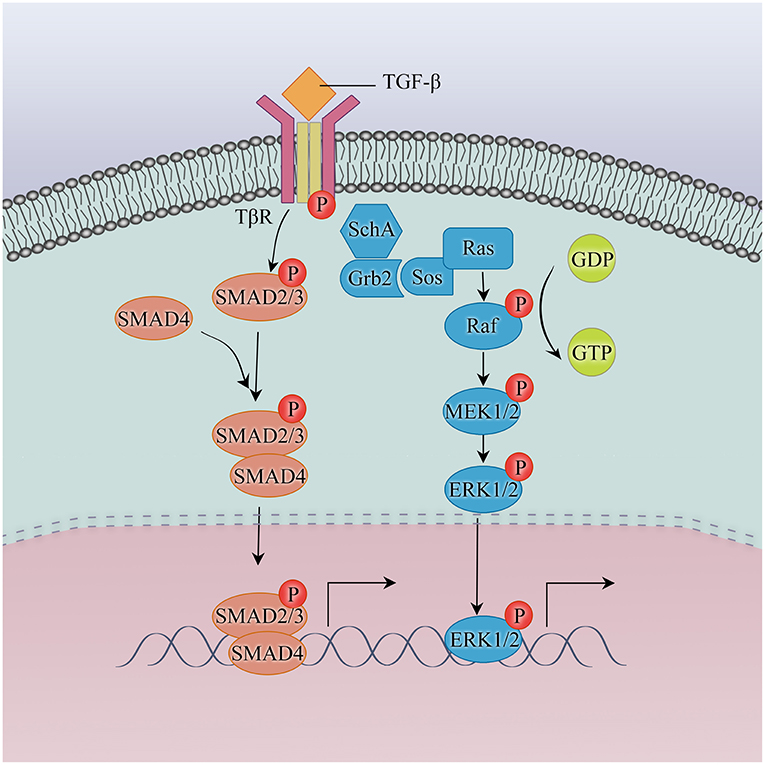
Non-small cell lung cancer-small cell lung cancer transformation as mechanism of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer

Mechanism of acquired T790m mutation and action of 3rd generation EGFR... | Download Scientific Diagram

Oncogenic drivers in nonsmall cell lung cancer and resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors

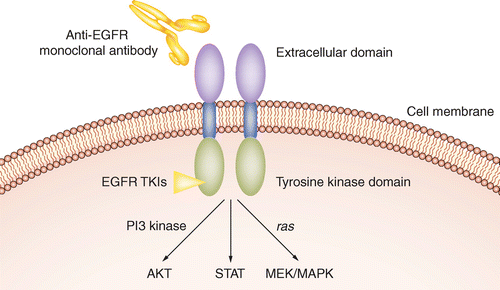
The challenge of targeting EGFR: experience with gefitinib in nonsmall cell lung cancer | European Respiratory Society

Repeat biopsy procedures and T790M rates after afatinib, gefitinib, or erlotinib therapy in patients with lung cancer - Lung Cancer
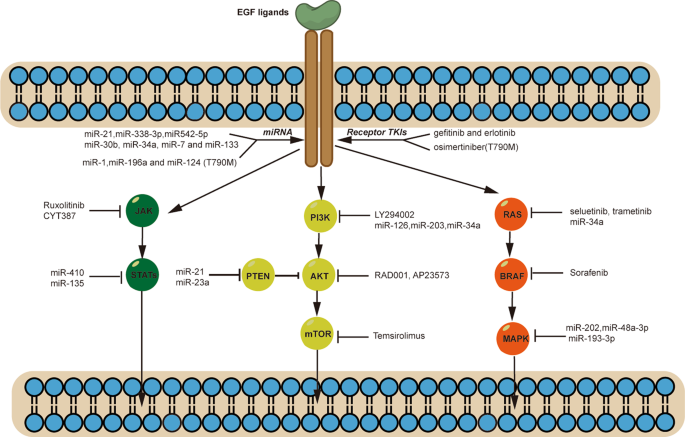
The emerging treatment landscape of targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy

Resistance to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer | Clinical Cancer Research

Identification of Ketene-Reactive Intermediate of Erlotinib Possibly Responsible for Inactivation of P450 Enzymes | Drug Metabolism & Disposition
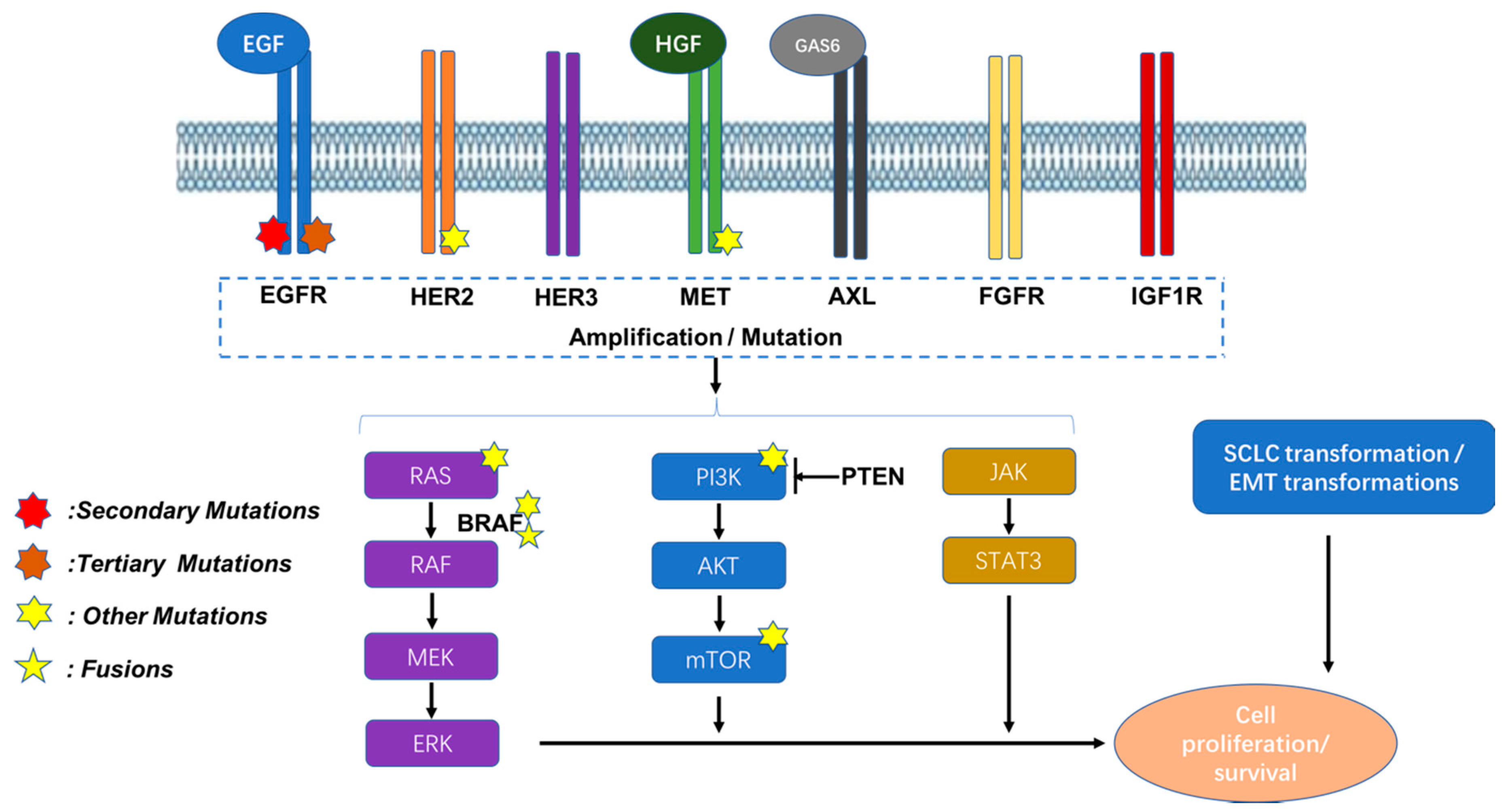
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Current Strategies for Treating NSCLC: From Biological Mechanisms to Clinical Treatment | HTML

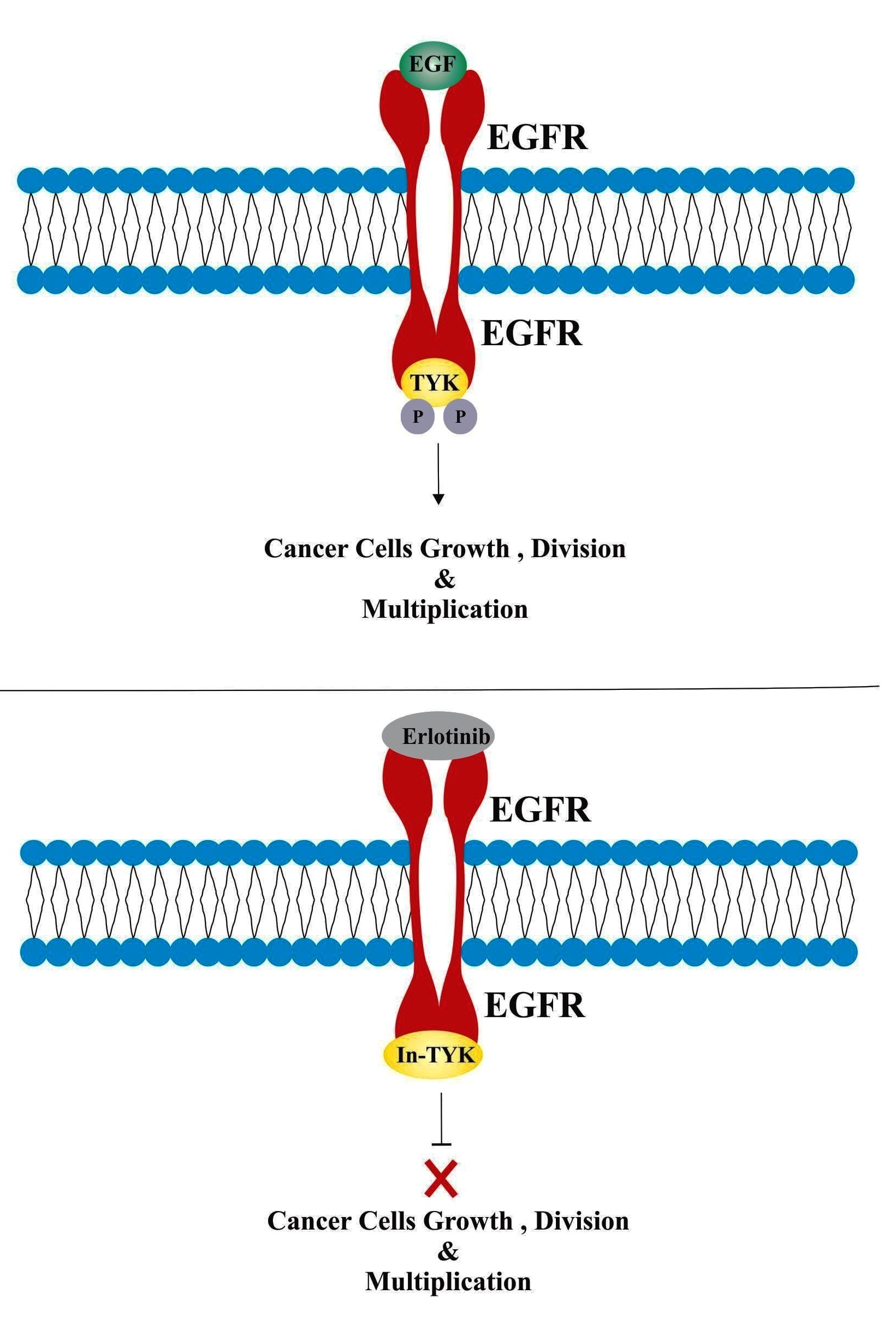
Action mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase... | Download Scientific Diagram
PLOS ONE: Mechanism of Resistance and Novel Targets Mediating Resistance to EGFR and c-Met Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Are erlotinib and gefitinib interchangeable, opposite or complementary for non-small cell lung cancer treatment? Biological, pha